Understanding the differences between watertight, weathertight, and fire doors is essential for ensuring safety onboard ships. Each type of door serves a unique function that contributes to the overall integrity and safety of the vessel, particularly in emergencies such as flooding, adverse weather conditions, and fires. This article will explore these doors’ characteristics, construction standards, and operational roles, emphasizing their significance in protecting ships and their crews.
Watertight Doors
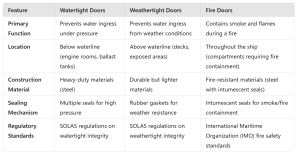
Definition and PurposeWatertight doors are designed to prevent the passage of water between compartments in a ship. According to the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), a watertight door must be capable of withstanding water pressure from both sides, making it essential for maintaining the vessel’s buoyancy and stability during flooding scenarios. These doors are typically installed in areas below the waterline, such as engine rooms, ballast tanks, and cargo holds. Watertight doors are constructed to rigorous standards to ensure their effectiveness. Key features include:
- Robust Materials: Made from steel or other durable materials that can withstand significant pressure.
- Sealing Mechanisms: Equipped with multiple seals (often rubber gaskets) to ensure a tight fit that prevents water ingress.
- Operational Mechanisms: Watertight doors can be manually operated or equipped with hydraulic or electric systems for ease of use.
Types of Watertight DoorsThere are primarily two types of watertight doors:
- Hinged Doors: These can be opened manually or automatically and are often used in areas where frequent access is needed.
- Sliding Doors: Typically operated hydraulically or electrically, these are often found in bulkheads where space is limited.


Weathertight Doors
Definition and PurposeWeathertight doors are designed to prevent water from entering the ship during adverse weather conditions but are not intended to withstand continuous submersion. These doors are typically found above the waterline—on decks and in areas exposed to rain, spray, or waves. Their primary function is to protect against weather-related ingress while allowing for ventilation and access.Construction StandardsWeathertight doors have different construction requirements compared to watertight doors:
- Material Composition: While still made from durable materials like steel or aluminum, they do not require the same thickness as watertight doors.
- Sealing Mechanisms: Weathertight doors utilize rubber gaskets and locking mechanisms (often called “dogs”) to ensure a secure seal against wind and rain.
- Design Features: Many weathertight doors include drainage systems to manage any water that may enter during heavy weather.


Fire Doors
Definition and PurposeFire doors play a critical role in fire safety onboard ships by preventing the spread of smoke and flames from one compartment to another. They are essential for protecting crew members and passengers during a fire emergency by containing fires within designated areas until they can be extinguished.Construction StandardsFire doors must meet stringent regulatory standards regarding fire resistance:
- Fire Ratings: Fire doors are assigned specific ratings (commonly 30, 60, 90, or 120 minutes) based on their ability to withstand fire exposure without compromising structural integrity.
- Materials Used: Typically constructed from steel or other fire-resistant materials, these doors may also incorporate intumescent seals that expand when exposed to heat, creating a tighter seal against smoke and flames.
- Self-Closing Mechanisms: Most fire doors are equipped with automatic closing devices that ensure they close immediately after being opened.
Key Differences Between Door Types
Maintenance Practices
Proper maintenance of watertight, weathertight, and fire doors is crucial for ensuring their functionality during emergencies:
- Regular Inspections: Crew members should conduct routine inspections at least once a month. This includes checking seals for wear and tear, ensuring operational mechanisms function correctly, and verifying that all locking mechanisms engage securely.
- Cleaning Procedures: Keeping door surfaces clean prevents corrosion and ensures proper sealing. Saltwater exposure can lead to degradation; therefore, rinsing with fresh water after exposure is essential.
- Testing Mechanisms: Regularly test hydraulic or electric operations to confirm they function correctly under emergency conditions. This includes testing self-closing mechanisms on fire doors.
All maintenance activities should be documented according to the vessel’s Planned Maintenance System (PMS) to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Case Studies Highlighting Importance
- MV Herald of Free Enterprise (1987): This tragic incident involved a ferry capsizing due to flooding caused by improperly closed bow doors. The failure of watertight integrity led to significant loss of life. This case underscores the importance of maintaining watertight doors and ensuring crew training on their operation.
- MS Costa Concordia (2012): The Costa Concordia disaster highlighted the importance of effective compartmentalization through watertight bulkheads and doors. Although many compartments were designed to contain flooding, improper management led to catastrophic consequences.
- Fire Incident on MV RoRo Vessel (2019): A fire broke out in an engine room compartment but was contained due to properly functioning fire doors that prevented smoke from spreading throughout the vessel. The quick response by crew members who utilized these barriers effectively saved lives.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between watertight, weathertight, and fire doors is critical for maintaining safety onboard ships. Each type of door serves a unique purpose—preventing flooding, protecting against weather elements, and containing fires—contributing significantly to overall maritime safety.By adhering to rigorous maintenance practices and regulatory standards set forth by SOLAS and other maritime organizations, ship operators can ensure that these vital components function effectively during emergencies. Training crew members in proper usage protocols further enhances preparedness for potential hazards at sea.In conclusion, investing in education about these door types not only protects vessels but also safeguards lives—an essential commitment for all maritime professionals navigating our oceans today.




Awesome! Its in fact remarkable post, I have got much clear idea on the topic of
from this article.