Maintain peak performance of your ship’s diesel generator with our expert guide to turbocharger cleaning and maintenance. Learn daily, weekly, and periodic procedures with practical steps, safety tips, and global best practices.
Why Turbocharger Maintenance Is Essential for Marine Diesel Generators
A turbocharger is one of the most vital components of a marine diesel generator. It increases the engine’s efficiency and power output by forcing more air into the combustion chamber. However, if not cleaned and maintained regularly, soot buildup and carbon deposits can lead to performance loss, increased fuel consumption, and potential breakdowns at sea.
Whether you’re a marine engineer, engine cadet, or OOW (Officer of the Watch), understanding how to clean and maintain a turbocharger is crucial for keeping operations safe and efficient. This article expands upon the procedures shown in the educational video, delivering deeper technical insights and international maintenance best practices.
Daily and Weekly Maintenance: Turbocharger Blower Washing
Daily Blower Washing
Daily blower washing is typically performed while the engine is running to remove light soot and dust from the compressor side of the turbocharger.
Procedure:
- Prepare a cleaning solution as per manufacturer guidelines.
- Open the blower washing valve.
- Use a hand pump to inject the cleaning agent.
- Allow the solution to flow for the recommended duration (typically 5–10 seconds).
- Close the valve after washing.
Ensure engine is running at a steady load and avoid starting or stopping the engine during cleaning.
Weekly Blower Washing
This process is similar but uses a stronger solution or a larger volume. Weekly cleaning helps remove stubborn buildup and prevents loss of boost pressure.
Always check:
- Boost air temperature: Keep within recommended values (usually below 200°C).
- Boost air pressure: Check against baseline engine parameters.
Periodic Maintenance: Turbine Side Cleaning (Every 200–250 Hours)
The turbine side of the turbocharger is more prone to carbon and soot accumulation. For safety and efficiency, clean this part every 200–250 operating hours.
Cleaning Procedure:
- Allow engine to cool down.
- Isolate and secure the turbocharger.
- Open the turbine washing valve.
- Inject water or cleaning agent using a hand pump.
- Let the turbine spin freely to distribute the solution.
- Drain any residual cleaning fluid.
- Close valve and perform a system check.
Important: Always refer to the turbocharger manufacturer (e.g., MAN, ABB, Mitsubishi) for approved chemicals and washing protocols.
Step-by-Step Valve Operation for Cleaning
Before Starting:
- Check oil pressure and turbocharger RPM.
- Make sure no abnormal noise or vibration exists.
Steps:
- Open drain valve to release existing residue.
- Open air or water injection valve.
- Inject cleaning solution using a dosing pump.
- Monitor pressure changes.
- Close valves in reverse order.
Repeat if needed, depending on soot level.
Final Checks & Best Practices
After Cleaning:
- Monitor boost air temperature and pressure.
- Check for smoke at exhaust (white or black smoke may indicate incomplete cleaning).
- Observe turbocharger RPM for fluctuations.
Best Practices:
- Keep a logbook of every cleaning session.
- Always wear PPE (gloves, goggles, mask).
- Follow STCW/IMO engine room safety protocols.

Real-World Example: Avoiding Turbocharger Failure
In 2023, a reefer vessel experienced turbocharger over-speeding and engine derating. Investigation found soot accumulation from improper washing practices. The engine had exceeded 400 hours without turbine cleaning.
Repairs cost over USD 25,000 and resulted in schedule delays.
Lesson: Follow the recommended 200–250 hour turbine cleaning cycle and document every cleaning.
FAQ: Turbocharger Maintenance on Marine Diesel Generators
1. Can I clean the turbocharger while the engine is running? Yes, blower side cleaning is designed for running conditions. Turbine side usually requires engine shutdown.
2. What cleaning solution should I use? Always refer to the engine/turbocharger maker’s guidelines (e.g., MAN, ABB).
3. How do I know if my turbocharger is dirty? Increased fuel consumption, reduced power, or high exhaust temperatures are key signs.
4. Can I skip weekly cleaning if daily washing is done? No. Daily washing removes light particles, while weekly cleaning tackles heavier buildup.
5. Is high-pressure air enough for cleaning? No. Use approved liquids. High-pressure air may damage delicate turbo parts.
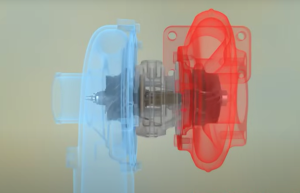
Conclusion: A Clean Turbocharger = Efficient Operation
Regular turbocharger maintenance ensures that your marine diesel generator runs efficiently, reliably, and safely. Neglecting it can lead to excessive fuel use, engine damage, or even forced shutdowns at sea.
By following this guide—daily blower washing, turbine cleaning every 200–250 hours, and valve operation procedures—you’ll maintain optimal engine health and extend equipment life. Clean turbochargers keep your vessel on schedule and your operations compliant with international standards.
References
- MAN Energy Solutions. (2023). Turbocharger Maintenance Guidelines. https://www.man-es.com
- ABB Turbocharging. (2023). Marine Turbocharger Cleaning Procedures. https://www.abb.com
- Wärtsilä. (2024). Turbocharger Operation and Maintenance Manual. https://www.wartsila.com
- IMO. (2023). STCW Code – Engine Room Procedures. https://www.imo.org
- DNV. (2023). Maritime Engine Health Monitoring. https://www.dnv.com


Incredible deep cleaning, exactly what we needed after renovation. Setting up regular service. Really impressed.