Global warming is one of the biggest environmental challenges faced by humanity today. The rise in temperatures caused by increased greenhouse gas emissions has far-reaching consequences for our planet’s ecosystems, and perhaps none are more affected than the world’s oceans and seas. The effects of global warming on our oceans and seas are both profound and far-reaching, and understanding these effects is essential for preserving the health and biodiversity of our planet.
One of the most immediate and visible impacts of global warming on our oceans is the rise in sea level. As the Earth’s temperature increases, glaciers and ice caps melt, adding to the volume of water in the oceans. Since the 19th century, the sea level has risen by about 8 inches, and this trend is expected to accelerate in the coming decades. As sea levels rise, low-lying areas and coastal regions are at risk of flooding and erosion, and this can cause significant damage to infrastructure, property, and people.
Another consequence of global warming on our oceans is the increasing acidification of seawater. As the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere rises, the oceans absorb a significant portion of it. This absorption leads to a chemical reaction that increases the acidity of seawater, and this can have serious consequences for marine life. Acidification can affect the ability of some organisms, such as shellfish and corals, to form and maintain their shells and structures. This can lead to reduced populations of these species, which can have ripple effects throughout the food chain.
In addition to acidification, global warming is also causing the oceans to warm, and this can have significant consequences for marine ecosystems. As the temperature of seawater rises, it can alter the distribution and migration patterns of many species of fish and other marine life. Some species may move to cooler waters, while others may become more prevalent in warmer areas. This can lead to imbalances in ecosystems and changes in the abundance and diversity of species.
Another impact of global warming on our oceans is the increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events. As the temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere rises, it can lead to more intense storms, hurricanes, and typhoons. These events can cause significant damage to coastal communities, ecosystems, and marine infrastructure, such as ports and shipping facilities.
The effects of global warming on our oceans and seas are complex and interconnected, and they are not limited to the physical environment. Global warming can also affect the livelihoods and well-being of people who rely on the oceans and seas for food, transportation, and recreation. Changes in fish populations and migration patterns can impact the fishing industry, while damage to coastal infrastructure can disrupt transportation and tourism.
In conclusion, global warming is having a profound impact on the world’s oceans and seas, and the consequences of this impact are far-reaching and complex. The rise in sea levels, ocean acidification, and warming waters are just a few of the many ways that global warming is affecting our oceans and the life they support. It is essential that we take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of global warming on our planet’s ecosystems, including the oceans and seas. By doing so, we can help to preserve the health and biodiversity of our planet for future generations.
Maritime Industry Contributes to Global Warming and Damaging Oceans
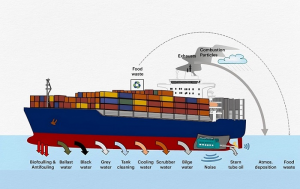
The shipping industry is a major contributor to global environmental issues, with a range of negative impacts on the world’s oceans and marine ecosystems. Some of the key environmental challenges associated with the shipping industry include:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The shipping industry is responsible for approximately 2.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Ships run on heavy fuels like bunker oil, which emit large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur oxide (SOx), nitrogen oxide (NOx), and particulate matter (PM) into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute to global warming and air pollution, which can have a range of negative impacts on human health and the environment.
- Ocean Acidification: The shipping industry is also a significant contributor to ocean acidification. Carbon dioxide emissions from ships dissolve in seawater, forming carbonic acid. This acidification of the oceans can damage marine ecosystems and impact the growth of shellfish and other marine organisms. This can have a cascading effect on the entire marine food chain, as marine organisms struggle to adapt to changing ocean conditions.
- Ballast Water: The ballast water that ships take on in one port and discharge in another can introduce invasive species into new habitats, causing harm to local ecosystems and species. When ships take on ballast water in one port and discharge it in another, they can inadvertently transport invasive species, which can cause harm to local ecosystems and species. This can lead to the displacement of native species, as well as the introduction of new diseases and parasites, which can have far-reaching impacts on marine ecosystems.
- Oil Spills: The transport of oil and other hazardous materials by ships poses a significant risk of oil spills, which can cause severe damage to marine habitats and wildlife. Even minor spills can have long-lasting effects on marine ecosystems, as oil can remain in the environment for years, affecting everything from plankton to whales. This can also have economic impacts, as fishing and tourism industries may be negatively affected by oil spills.
- Noise Pollution: The noise generated by ships can be harmful to marine mammals and disrupt their behavior, including their ability to communicate, navigate, and find food. This can lead to stress and behavioral changes, which can have long-term impacts on marine mammal populations.
Overall, the shipping industry needs to adopt cleaner and more sustainable practices to mitigate its impact on the environment. This includes using low-emission fuels, reducing waste and pollution, and implementing measures to prevent oil spills and invasive species. Additionally, measures should be taken to reduce noise pollution and minimize the industry’s contribution to ocean acidification. By taking these steps, the shipping industry can help to reduce its impact on the environment and protect the world’s oceans and seas.

