Rankine Cycle and Its Improvement in Marine Systems
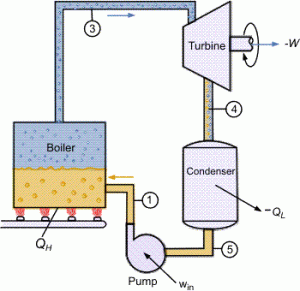
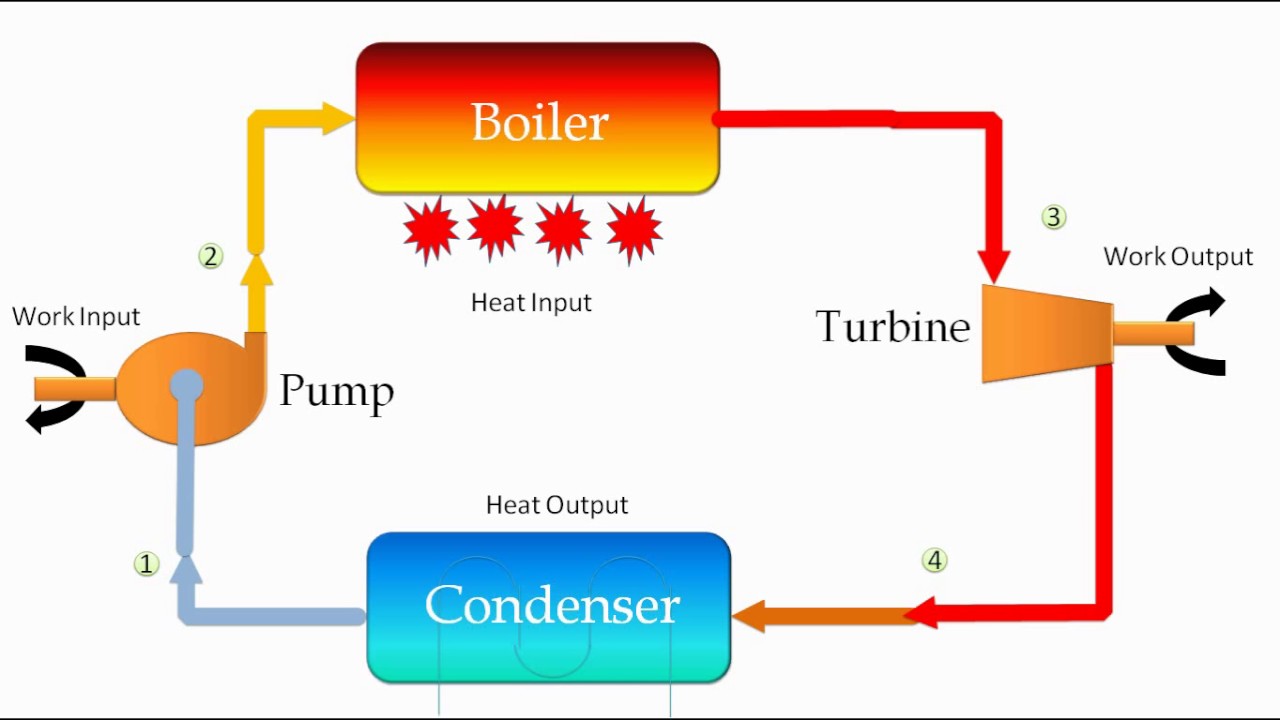
The system shown in the below image illustrates a typical Rankine cycle setup used onboard some ships. This system can be configured in various ways: the steam turbine can serve as the main propulsion engine, a steam turbo generator to produce electricity, or a cargo steam turbo-pump. Understanding this system is crucial for marine engineers and ship cadets, as it comprises several vital components that are essential for efficient and safe ship operation. The four main components of this system are the boiler, steam turbine, condenser, and feedwater pump.
Main Components:
- Boiler: Generates high-pressure steam by heating water.
- Steam Turbine: Converts thermal energy from steam into mechanical energy for propulsion or electricity generation.
- Condenser: Cools and condenses the exhaust steam from the turbine back into water.
- Feedwater Pump: Pumps the condensed water back into the boiler to complete the cycle.
The Rankine cycle is the fundamental operating principle behind marine steam turbines, involving the conversion of water into steam, which is then used to produce mechanical energy. This cycle is composed of several key stages:
- Steam Generation: Water is heated in the boiler to produce high-pressure steam. The boiler heats the water by burning fuel, converting the thermal energy into steam at high pressure and temperature. This steam is then directed towards the turbine.
- Expansion: The high-pressure steam expands through the turbine, generating mechanical energy. As the steam passes through the turbine blades, it loses pressure and temperature but imparts kinetic energy to the blades, causing them to rotate. This rotation drives the turbine shaft, which is connected to the ship’s propeller or generators.
- Condensation: After doing work in the turbine, the low-pressure steam is condensed back into water in the condenser. This stage involves cooling the steam, typically using seawater, to convert it back into liquid form. The condensed water is collected in a hotwell or a condensate tank.
- Pumping: The condensed water is then pumped back into the boiler using feedwater pumps, completing the cycle. The feedwater is often preheated before entering the boiler to improve the efficiency of the cycle.
Practical Improvements on Board
To enhance the efficiency and performance of the Rankine cycle on board ships, several practical improvements can be implemented:
- Superheating the Steam: Increasing the temperature of the steam beyond its boiling point, known as superheating, can significantly enhance the efficiency and power output of the steam turbine. Superheaters are used to raise the temperature of the steam after it leaves the boiler, which reduces the moisture content and increases the thermal efficiency of the cycle. Superheated steam ensures that the steam remains dry during expansion, preventing damage to the turbine blades and improving overall performance.
- Reheating: In a reheat Rankine cycle, the steam is reheated between turbine stages to reduce moisture content and improve efficiency. After the steam has partially expanded in the high-pressure turbine, it is returned to the boiler and reheated to a higher temperature. The reheated steam then enters the intermediate or low-pressure turbine stages. Reheating helps to maintain a higher average temperature during the expansion process, reducing the moisture content in the later stages of expansion and improving the overall efficiency of the cycle.
- Regenerative Feedwater Heating: Using extracted steam from various points in the turbine to preheat the feedwater before it enters the boiler is known as regenerative feedwater heating. This process increases the temperature of the feedwater, reducing the amount of fuel needed to convert it into steam. Feedwater heaters are used to transfer heat from the extracted steam to the feedwater, thereby improving the thermal efficiency of the boiler and reducing fuel consumption. Regenerative feedwater heating can also decrease the thermal stress on the boiler, extending its lifespan.
Marine Boilers on Ships
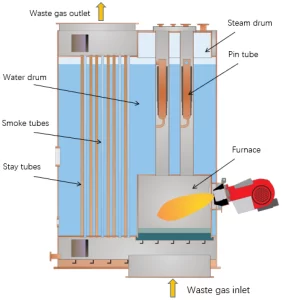
Marine boilers are critical components in steam-powered ships, responsible for generating the high-pressure steam needed to drive steam turbines. These boilers operate by heating water to its boiling point, producing steam at high pressure and temperature. The generated steam is then directed into turbines, where its energy is converted into mechanical motion.
The furnace is where fuel combustion occurs, designed to maximize the transfer of heat to the water. Water and steam drums are integral to water-tube boilers, helping to separate steam from water and maintain appropriate water levels. Modern marine boilers use efficient burners to ensure complete fuel combustion, optimizing heat production and reducing emissions. Economizers are heat exchangers that preheat the feedwater entering the boiler, utilizing waste heat from exhaust gases to improve overall efficiency. Superheaters increase the temperature of steam above its saturation point, enhancing the thermal efficiency of the steam turbine.
Marine boilers typically operate at high pressures and temperatures to maximize efficiency:
- Pressure: Marine boilers can operate usually at pressures ranging from 5 to 60 bar, depending on the type and design of the boiler.
- Temperature: The steam temperature in marine boilers often ranges from 250°C to 550°C, depending on the saturated/superheated pressure.
]Types of Marine Boilers
- Fire-Tube Boilers: In these boilers, hot gases pass through tubes surrounded by water. They are relatively simple in design and easy to maintain. However, their capacity and efficiency are generally lower compared to other types.
- Water-Tube Boilers: These boilers feature water-filled tubes that are heated externally by combustion gases. They are capable of generating higher pressure steam and are more efficient, making them suitable for larger ships and more demanding applications.
- Composite Boilers: Combining features of fire-tube and water-tube boilers, composite boilers offer flexibility and efficiency. They are often used in ships with multiple steam requirements, such as cargo heating and power generation.
Alfa Laval is known for producing efficient and reliable marine boilers, providing solutions for both new ships and retrofits, including Aalborg marine boilers. Saacke GmbH specializes in marine combustion systems and boilers, offering high-performance products designed for the maritime industry. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries produces advanced marine boiler solutions with a focus on high efficiency and reliability. Miura Boilers provides compact, efficient marine boilers, emphasizing safety and ease of maintenance. Kangrim Heavy Industries is a prominent manufacturer of marine boilers, known for their durability and advanced technology.
Marine Steam Turbine on Ships
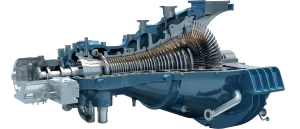
Marine steam turbines are among the oldest types of propulsion engines, converting thermal energy from steam into mechanical energy to move a ship’s propeller. While their usage has decreased with technological advancements, they remain prevalent in naval ships and some merchant vessels due to their reliability and power-to-weight ratio. Steam turbines are also used in combined propulsion systems with diesel engines or gas turbines to enhance efficiency.
There are two main types of marine steam turbines: impulse turbines, where steam expands in nozzles and maintains constant pressure across moving blades, and reaction turbines, where both fixed and moving blades act as nozzles, resulting in a pressure drop across both.
Key manufacturers of marine steam turbines include MAN Energy Solutions, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and General Electric.
Safe operation of marine steam turbines is essential to prevent accidents and extend machinery life. This involves monitoring parameters such as steam pressure, temperature, and vibration levels, ensuring continuous lubrication, and following strict start-up and shut-down procedures to avoid thermal stresses.
The operation of a marine steam turbine involves generating steam in a boiler, expanding it through the turbine to cause rotation, and then condensing the exhaust steam back into water to complete the cycle.
Common issues with marine steam turbines include erosion, vibration, overheating, and corrosion. Regular maintenance and inspections are crucial to identify potential problems early, maintain efficiency, and ensure smooth operation. This includes routine checks for wear, corrosion, and deposits, periodic cleaning of turbine blades, and testing and replacing lubricating oil as needed.
Marine steam turbines have played a significant role in ship propulsion for many years. Despite the prevalence of modern propulsion methods, understanding the operation and maintenance of steam turbines is crucial for ships that still utilize this technology, ensuring their longevity and safe operation on the high seas.
Marine Feedwater Pumps
Feedwater pumps are an integral part of marine steam systems, ensuring continuous water circulation through the boiler and the entire Rankine cycle. These pumps move the feedwater from the hotwell or condenser back into the boiler, where it can be reheated and converted into steam. There are different types of feedwater pumps, including centrifugal and positive displacement pumps. Centrifugal pumps are commonly used due to their ability to handle large volumes of water and their relatively simple design, converting rotational kinetic energy from an electric motor into hydrodynamic energy of the water flow. Positive displacement pumps, which include piston pumps, diaphragm pumps, and gear pumps, move a fixed amount of water with each cycle and are typically used when a constant flow rate is needed, regardless of the system’s pressure.
Feedwater pumps must handle high pressures to ensure water is effectively circulated back into the high-pressure environment of the boiler. They need to operate efficiently to reduce the overall energy consumption of the steam system, thus saving fuel and operational costs. Additionally, reliability is crucial, as continuous and reliable operation prevents interruptions in the steam cycle, which could lead to system failures or reduced efficiency.
Maintenance of feedwater pumps involves regular inspections to check for wear and tear, leaks, and other signs of damage. Proper lubrication is necessary to prevent overheating and excessive wear of moving parts. Seals must be maintained to prevent leaks and ensure pressure is kept at optimal levels. Continuous performance monitoring is essential to detect any efficiency losses or mechanical issues early on, ensuring the pump operates effectively and reliably.

In-line Vertical Multistage Pump – CARVER
Steam Dumping Condenser
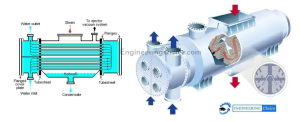
A steam dumping condenser is a critical component in marine steam systems, designed to handle excess steam by condensing it back into water. This process maintains system balance and prevents overpressure conditions. The steam dumping condenser helps in maintaining the system pressure within safe limits by condensing excess steam, thus preventing potential damage. It improves the overall thermal efficiency of the steam system by condensing steam and returning the water to the cycle. In some systems, the heat extracted during condensation is used to preheat the feedwater, further enhancing efficiency.
Key components of a steam dumping condenser include a cooling water supply, typically using seawater as the cooling medium, and a heat exchanger where the steam passes through a series of tubes or plates, transferring heat to the cooling water and condensing into liquid. The condensed water, known as condensate, is collected and returned to the hotwell or directly to the feedwater system.
Maintenance of steam dumping condensers involves regular cleaning of the heat exchanger surfaces to remove fouling and ensure efficient heat transfer. It is essential to inspect for leaks in the tubes or seals to prevent mixing of steam and cooling water. Monitoring temperature and pressure ensures the condenser operates efficiently, maintaining the balance and efficiency of the marine steam system.
By understanding the functions and maintenance of marine feedwater pumps and steam dumping condensers, marine engineers and ship cadets can ensure the effective and efficient operation of shipboard steam systems, maintaining the reliability and performance of marine propulsion and auxiliary systems.
Here are seven open-ended questions based on the provided above guide for ship engineers and marine engineering cadets:
- How do the different components of the Rankine cycle (boiler, steam turbine, condenser, and feedwater pump) interact to maintain a continuous cycle, and what are the critical considerations for each component’s operation on board a ship?
- What are the primary challenges associated with maintaining marine boilers, and how can the introduction of economizers and superheaters improve boiler efficiency and operational lifespan?
- Describe the impact of superheating and reheating steam on the efficiency and performance of steam turbines. How do these processes help reduce moisture content and enhance the overall cycle efficiency?
- How does regenerative feedwater heating contribute to fuel efficiency and thermal stress reduction in marine boilers? What are the potential drawbacks or challenges associated with this technique?
- What factors determine the choice between centrifugal and positive displacement feedwater pumps in marine steam systems? Discuss the maintenance requirements and operational challenges of each pump type.
- How does a steam dumping condenser maintain system balance and prevent overpressure conditions in marine steam systems? What are the best practices for maintaining the efficiency and reliability of steam dumping condensers?
- With the shift towards more advanced propulsion methods, what are the key advantages and limitations of traditional steam turbines in modern marine applications? How can ship engineers ensure the longevity and efficiency of steam turbines still in use?
By Dr R.Karimpour

Very nice article