Learn how marine diesel engine generators power ships at sea. Discover their components, operation, and maintenance practices crucial for safe, efficient maritime operations.

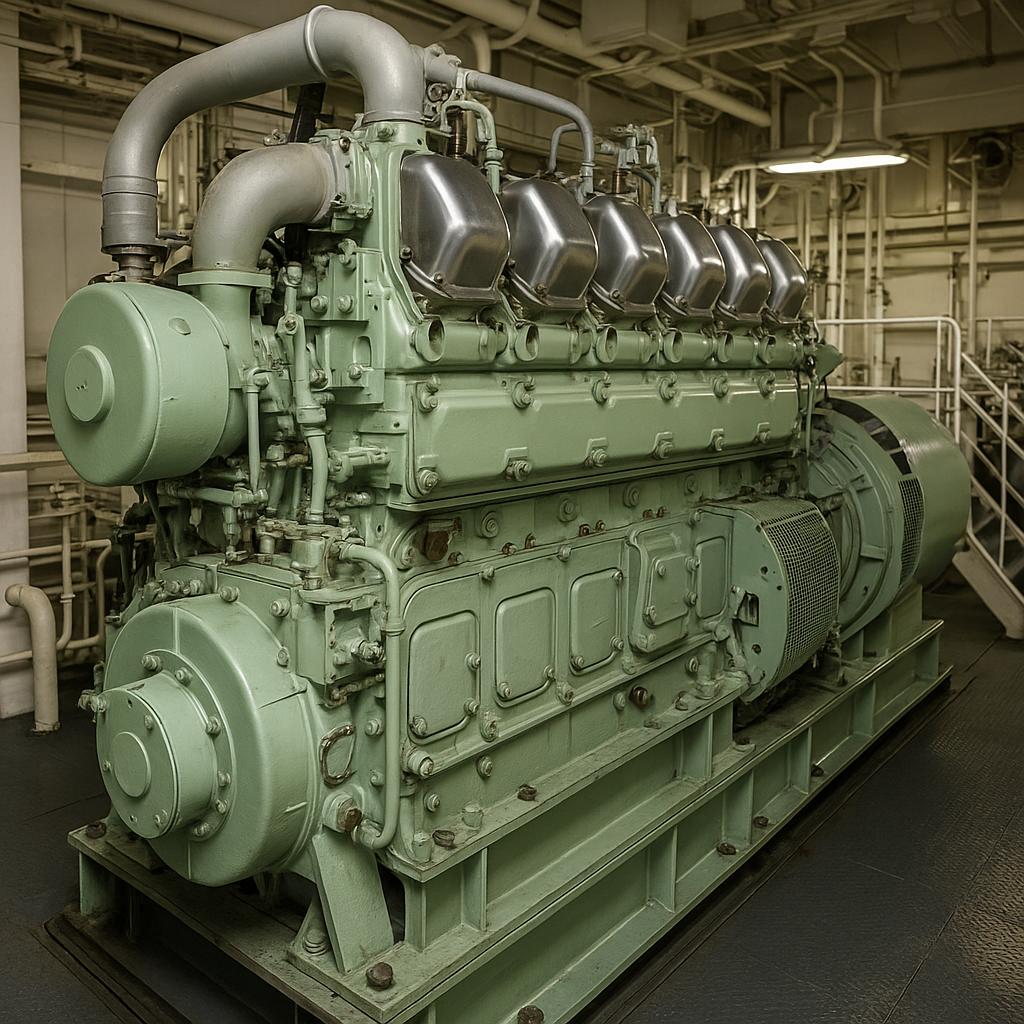
The world of shipping and maritime activity depends heavily on the power generated onboard the vessels for smooth and efficient operations. Marine diesel engine generators, an integral part of a ship’s power generation system, provide the necessary electrical power to run numerous critical and non-critical systems on board. This article aims to provide a thorough understanding of marine diesel engine generators, their components, operation, and maintenance.
Understanding of Marine Diesel Engine Generators
Marine diesel engine generators are more than just critical components of a ship; they are the very lifeblood that ensures the ship’s operational capability while at sea. They provide the electrical power that keeps the ship’s various systems functioning. Whether it’s the onboard lighting system, machinery, navigation systems, communication systems, or propulsion systems, marine diesel engine generators play a pivotal role. These generators derive their power from the ship’s diesel fuel reserves, making them an efficient and effective solution for maritime power generation. To understand them more fully, we need to look at the nature of their operation, design characteristics, and their inherent advantages.
How Marine Diesel Engine Generators Operate
The core operation of marine diesel engine generators revolves around the concept of energy transformation. The energy stored in the chemical bonds of diesel fuel is first converted into mechanical energy by the process of internal combustion within the engine. The combustion process generates heat, causing a rapid expansion of gases which pushes the pistons inside the engine. This movement is then converted into rotary motion by the engine’s crankshaft.
Attached directly to the crankshaft is the rotor of the alternator, which spins synchronously with the engine’s rotations. The rotor, being an electromagnet, creates a magnetic field that cuts across the conductive windings of the alternator’s stator, inducing an electromotive force (EMF). This results in the flow of alternating current (AC) in the generator’s circuit. The electricity generated is then used to power all the electrical systems on board the ship, from basic amenities such as lighting and heating, to critical systems such as navigation, communication, and propulsion.
Design Characteristics of Marine Diesel Engine Generators
Marine diesel engine generators are designed to withstand the harsh and challenging maritime conditions. They must operate effectively amidst the continuous vibrations, saline air, and varying load demands characteristic of seafaring vessels. Therefore, they are built robust and compact to ensure reliability, longevity, and efficient utilization of space on board the ship.
Moreover, these generators are designed to ensure optimum fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, abiding by the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) stringent regulations. Features like turbocharging and aftercooling are integrated into the engine design to increase power output, improve fuel economy, and reduce exhaust emissions.
Components of Marine Diesel Engine Generators
Marine diesel engine generators are complex systems comprising several key components:
- Diesel Engine: This is the prime mover, responsible for converting the chemical energy in diesel fuel into mechanical energy. This energy is used to drive the generator.
- Alternator: Connected directly to the engine, the alternator’s role is to convert the mechanical energy from the diesel engine into electrical energy. It does this by generating alternating current (AC) through electromagnetic induction.
- Cooling System: Given the heat generated by the engine during operation, a cooling system is vital. This often consists of a combination of a water coolant system and an air ventilation system.
- Fuel System: This system manages the supply of diesel fuel to the engine, including storage, transfer, and injection into the combustion chambers.
- Exhaust System: The exhaust system expels the combustion gases safely from the engine, minimizing environmental impact.
- Control System: The control system regulates the operation of the generator, including starting/stopping the engine, speed control, load sharing, and fault detection.
Maintenance of Marine Diesel Engine Generators
Routine maintenance is a critical aspect of ensuring the reliable operation of marine diesel engine generators. Some key aspects of maintenance include:
- Routine Checks: Regular checks should be carried out on the generator’s systems, particularly for signs of wear and tear, unusual noises or vibrations, and potential leaks of fuel, oil, or coolant.
- Lubrication: Regular lubrication of moving parts is critical to minimizing friction and subsequent wear and tear.
- Cooling System Maintenance: The cooling system should be kept clean and free of obstructions, and coolant levels and quality should be monitored regularly.
- Fuel System Maintenance: Fuel filters should be checked and replaced as necessary, and fuel quality should be monitored to avoid damage to the engine.
- Exhaust System Maintenance: Regular checks should be carried out to ensure there are no blockages or leaks in the exhaust system, which could lead to harmful gases being released into the environment or the engine room.
- Electrical System Checks: Regular checks and maintenance should be carried out on the alternator and other electrical components, including the control system and wiring, to ensure they are in good working order.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is a marine diesel engine generator?
A marine diesel engine generator is a power generation unit that uses diesel fuel to produce electricity on ships, supporting essential systems like lighting, navigation, and propulsion.
Q2: How does a marine diesel engine generator work?
It converts chemical energy from diesel fuel into mechanical energy through combustion, then into electrical energy via an alternator, supplying AC power to onboard systems.
Q3: Why are marine diesel generators critical for ships?
They ensure operational reliability by powering all vital shipboard systems, including emergency equipment, making them essential for safety and functionality at sea.
Q4: What are the key components of a marine diesel generator?
Core components include the diesel engine, alternator, cooling system, fuel system, exhaust system, and control system.
Q5: How is maintenance performed on a marine diesel generator?
Maintenance includes regular inspections, lubrication, cooling system upkeep, fuel quality checks, exhaust system checks, and electrical diagnostics to prevent breakdowns.
Q6: Are marine diesel generators regulated for emissions?
Yes. They must meet IMO regulations for fuel efficiency and emissions control, often using turbocharging and aftercooling technologies to comply.
Q7: What makes marine diesel generators different from land-based ones?
They are designed to handle the harsh marine environment, with features like corrosion-resistant materials, compact design, and vibration resistance.
📚 References
-
Calder, Nigel. Marine Diesel Engines: Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Repair. McGraw-Hill Education, 2021.
-
Sname (Society of Naval Architects and Marine Engineers). Principles of Naval Engineering.
-
IMO (International Maritime Organization). MARPOL Annex VI: Regulations for the Prevention of Air Pollution from Ships.
-
MAN Energy Solutions. Marine Engines and Systems. https://www.man-es.com/
-
Wärtsilä. Marine Power Solutions. https://www.wartsila.com/
-
DNV. Maritime Advisory on Marine Generator Systems. https://www.dnv.com/maritime