Ports are vital nodes in global trade and logistics, serving as gateways for the movement of goods and commodities worldwide. In the face of growing trade volumes, increasing vessel sizes, and stringent environmental regulations, ports must evolve to remain competitive and efficient. Technological innovations are at the forefront of this transformation, driving advancements in port operations and management. This article explores the challenges of port operations, the role of technology in addressing these challenges, and key innovations such as digitalization and smart ports, supported by real-world case studies.
Understanding Port Operations and Their Challenges
Modern ports are complex ecosystems involving multiple stakeholders, including terminal operators, shipping lines, freight forwarders, customs authorities, and transport companies. Managing these interconnected operations requires seamless coordination to ensure the smooth handling of cargo. Despite advancements in infrastructure, ports face several challenges:
- Congestion and Capacity Constraints: Growing trade volumes lead to bottlenecks, particularly in high-traffic ports, reducing efficiency and increasing turnaround times.
- Environmental Impact: Ports contribute to air and water pollution through emissions from vessels, cargo handling equipment, and associated transportation.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Legacy systems and processes often result in delays, miscommunication, and suboptimal resource utilization.
- Security Risks: Cybersecurity threats and physical risks to cargo and infrastructure remain pressing concerns.
Addressing these challenges requires a paradigm shift in how ports operate, leveraging technology to optimize processes and enhance sustainability.

The Role of Technology in Optimizing Port Logistics
Technology has become a cornerstone of modern port operations, enabling ports to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact. By integrating advanced systems and automation, ports can achieve higher levels of efficiency and reliability. Key areas where technology has significantly impacted port logistics include:
1. Automation of Cargo Handling
Automated cranes, guided vehicles, and robotic systems are revolutionizing cargo handling by improving speed and accuracy while reducing labor costs. For example, the Port of Rotterdam employs automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to transport containers within terminals, achieving precise movement and reduced downtime.
2. Predictive Maintenance
IoT sensors and data analytics allow ports to monitor equipment and infrastructure in real time. Predictive maintenance systems forecast potential failures, enabling timely repairs and reducing unplanned downtime. The Port of Antwerp uses predictive analytics to monitor quay walls and prevent structural failures, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
3. Energy Optimization
Innovative technologies are also helping ports reduce their carbon footprint. Shore power systems, for instance, allow ships to connect to the port’s electrical grid while docked, reducing emissions from auxiliary engines. The Port of Los Angeles has implemented shore power across its terminals, cutting nitrogen oxide emissions by 95%.
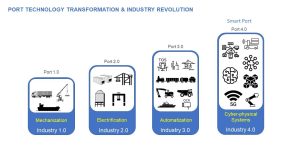
Digitalization in Ports: Smart Ports and Port 4.0 Concepts
Digitalization represents a transformative force in port operations. The concepts of “Smart Ports” and “Port 4.0” embody the integration of digital technologies, automation, and data-driven decision-making to create highly efficient, sustainable, and connected port ecosystems.
Smart Ports: A Vision of Connectivity
Smart ports leverage IoT, artificial intelligence (AI), and big data to enable real-time monitoring and decision-making. These technologies facilitate:
- Dynamic Resource Allocation: AI-powered algorithms optimize the use of cranes, berths, and storage areas based on real-time demand.
- Enhanced Traffic Management: IoT devices and traffic control systems streamline vessel movements, reducing waiting times and fuel consumption.
- Data Sharing Platforms: Collaborative platforms connect stakeholders, providing transparency and improving supply chain visibility.
The Port of Hamburg serves as a prime example of a smart port. Its smartPORT logistics platform integrates data from shipping lines, trucking companies, and rail operators, enabling real-time tracking and efficient coordination. This approach has significantly reduced congestion and improved overall logistics efficiency.
Port 4.0: Aligning with Industry 4.0 Principles
Port 4.0 extends the smart port concept by aligning port operations with Industry 4.0 principles, focusing on advanced automation, cyber-physical systems, and blockchain technology. Key features of Port 4.0 include:
- Blockchain for Secure Transactions: Blockchain enhances transparency and security in port operations, streamlining documentation and reducing fraud. The Port of Valencia has piloted a blockchain-based platform for managing shipping documentation, cutting processing times by 80%.
- Digital Twins: Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical port assets, enabling predictive modeling and scenario analysis. The Port of Singapore employs digital twins to simulate port layouts and optimize infrastructure planning.
–
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Port Innovations
Case Study 1: Rotterdam – A Pioneer in Digital Transformation
The Port of Rotterdam, Europe’s largest port, has embraced digital transformation through its PortXchange platform. This digital collaboration platform integrates data from shipping lines, terminal operators, and hinterland transport providers, facilitating optimized vessel scheduling. By reducing idle time and streamlining operations, the port has cut carbon emissions by 20%.
Additionally, Rotterdam has deployed autonomous drones for surveillance and inspection tasks, enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
Case Study 2: Los Angeles – A Leader in Sustainability
The Port of Los Angeles has emerged as a leader in sustainable port operations. Through its Clean Air Action Plan, the port has implemented several technological innovations, including:
- Zero-Emission Equipment: Electric yard tractors and cranes are replacing diesel-powered equipment.
- Energy-Efficient Lighting: LED lighting systems reduce energy consumption across port facilities.
The port also collaborates with tech companies to deploy AI solutions for optimizing container movement, further improving efficiency.
Case Study 3: Singapore – Setting the Standard for Automation
Singapore’s Tuas Mega Port, slated for completion in 2040, represents the pinnacle of port automation. The port features:
- Automated Yard Operations: Cranes and AGVs handle containers autonomously, ensuring precision and speed.
- Integrated Command Centers: A centralized system monitors and controls all operations, minimizing disruptions.
Tuas is designed to handle up to 65 million TEUs annually, making it the world’s largest fully automated terminal.
In conclusion, technological innovations are reshaping the landscape of port operations, addressing long-standing challenges and unlocking new efficiencies. From automation and predictive maintenance to smart port concepts and Port 4.0 initiatives, technology offers a path toward sustainable and competitive port management. Real-world examples, such as Rotterdam, Los Angeles, and Singapore, highlight the transformative impact of these innovations. As ports continue to adopt advanced technologies, collaboration among stakeholders and investment in research and development will be critical to realizing the full potential of digitalization. By embracing these innovations, ports can not only meet the demands of global trade but also contribute to a more sustainable and connected maritime future.