Cryptocurrency, with its decentralized digital structure, is increasingly playing a significant role in reshaping global trade and maritime transport. Offering advantages like enhanced security, transparency, faster transactions, and reduced costs, cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology have the potential to revolutionize maritime logistics and international commerce.
Cryptocurrency and Blockchain: A Brief Overview
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, along with stablecoins such as Tether, are revolutionizing global trade through blockchain technology. This decentralized digital ledger system creates tamper-proof transaction records, offering maritime logistics unprecedented security and transparency. By eliminating paperwork bottlenecks and reducing fraud potential, blockchain stands to dramatically streamline shipping documentation, cargo tracking, and international payments across the maritime industry.
Benefits of Cryptocurrency in Maritime Trade
Digital currencies provide four transformative advantages for shipping: instant cross-border payments that bypass slow bank processing, dramatically lower transaction fees through disintermediation, immutable cargo provenance tracking via blockchain, and financial access for emerging market traders excluded from traditional banking. These innovations collectively address longstanding pain points in maritime commerce, from costly delays to documentation fraud, while creating new opportunities for supply chain financing and automated compliance
1. Faster and Secure Transactions
Traditional international trade involves extensive paperwork and banking processes, taking days or weeks. Cryptocurrencies facilitate almost instantaneous transactions, enabling quicker turnaround in payments and shipments.
2. Reduced Transaction Costs
Cryptocurrencies bypass intermediary banks, significantly cutting transaction fees. These savings can improve profitability for maritime companies, freight forwarders, and global traders.
3. Enhanced Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain-based systems provide transparent tracking of goods from origin to destination, reducing fraud and ensuring cargo authenticity, provenance, and compliance with international regulations.
4. Financial Inclusion
Cryptocurrency opens opportunities for traders in countries with limited access to traditional banking infrastructure, enabling smoother participation in global maritime commerce.
PORT MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY INADEQUACY, Credit: https://www.ippo-engineering.eu/en/blockchain-technology-in-maritime-trade/
Current Applications in Maritime Transport
Leading shipping companies already deploy blockchain solutions like Maersk’s TradeLens for real-time cargo monitoring, while smart contracts automatically execute agreements upon delivery confirmation. The digital Bill of Lading eliminates document forgery risks, and blockchain-based insurance platforms accelerate claims processing with verifiable damage records. These implementations demonstrate how distributed ledger technology is solving specific challenges in vessel operations, port logistics, and trade finance.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain-based smart contracts automate maritime agreements, reducing the risk of disputes and speeding up contract execution.
- Cargo Tracking and Management: Platforms like TradeLens (a blockchain initiative by Maersk and IBM) leverage blockchain to track cargo efficiently.
- Digital Bill of Lading (B/L): Blockchain digitizes the Bill of Lading, reducing document fraud, delays, and mismanagement in cargo transfers.
- Insurance and Claims Processing: Blockchain streamlines insurance claims for lost or damaged cargo through transparent and tamper-proof data records.
Blockchain in Maritime Industry
Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force across various industries, including the maritime sector. The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain, as illustrated in the attached images, brings enhanced transparency, security, and efficiency to maritime operations.
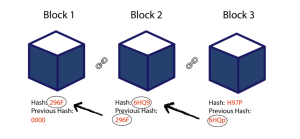
How Blockchain Works in Maritime
The image Block-Chain-01-1024×659.png demonstrates the fundamental structure of a blockchain:
- Block 1 contains data (e.g., shipment details) and a unique Hash (296F), with a Previous Hash (0000) indicating it is the first block.
- Block 2 references Block 1’s hash (296F), ensuring data integrity. Any alteration in Block 1 would invalidate Block 2’s Previous Hash (6HQ9), exposing tampering.
- Block 3 continues this chain, linking back to Block 2 (6HQ9), creating an unbreakable, auditable ledger.
The hash-example.png further emphasizes how each block’s hash is derived from its data and the previous block’s hash, making fraud virtually impossible.
Key Applications of Blockchain in Maritime
- Supply Chain Transparency
- Real-time tracking of cargo from origin to destination.
- Immutable records of shipping documents such as Bills of Lading.
- Enhanced traceability of goods, reducing fraud and theft.
- Smart Contracts for Maritime Transactions
- Automated execution of shipping contracts, insurance claims, and port payments.
- Reduces reliance on intermediaries.
- Enhances trust among stakeholders (shippers, port authorities, freight forwarders).
- Crew Certification and Training Validation
- Secure, verifiable records of crew qualifications and training.
- Easy cross-border validation for international compliance.
- Reduces administrative overhead and paperwork.
- Maintenance Logs and Vessel History
- Transparent maintenance records for ships.
- Helps in vessel valuation and safety compliance.
- Assists classification societies in auditing and surveys.
- Customs and Regulatory Compliance
- Streamlines customs processes by sharing trusted data with authorities.
- Facilitates rapid inspections and verifications.
- Enhances compliance with international maritime regulations (IMO, SOLAS, MARPOL).
Benefits of Blockchain
- Security: Cryptographic hashing ensures data integrity.
- Transparency: All parties have access to a single version of the truth.
- Efficiency: Reduced paperwork and processing time.
- Trust: Builds confidence among maritime stakeholders.
Challenges and Considerations
- Integration with legacy maritime IT systems.
- Standardization across ports and shipping companies.
- Regulatory acceptance and legal frameworks.
- Training maritime professionals on blockchain usage.
The adoption of blockchain in the maritime industry is expected to grow as stakeholders seek secure and efficient digital solutions. Collaboration among technology providers, regulators, and industry players is crucial to unlocking its full potential. Blockchain presents a promising pathway for digital transformation in the maritime industry. By enabling secure, transparent, and efficient operations, it supports safer navigation, sustainable practices, and global maritime trade resilience.
Challenges and Risks
Despite its potential, crypto adoption faces significant hurdles including regulatory fragmentation across maritime jurisdictions, the price volatility of non-stable coin assets, and sophisticated cyber threats targeting digital wallets. Many shipping firms remain cautious due to unclear taxation policies and the energy intensity of some blockchain networks, though emerging solutions like carbon-neutral cryptocurrencies and regulatory sandboxes are gradually addressing these concerns.
Despite these benefits, cryptocurrencies in maritime trade face challenges:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear regulatory frameworks internationally can limit widespread adoption.
- Market Volatility: Price fluctuations in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin can introduce financial risk. Stablecoins help mitigate this risk.
- Cybersecurity Concerns: Digital currencies are vulnerable to cyberattacks, requiring robust security systems.
Future Outlook
The maritime sector is poised for accelerated blockchain integration as international standards emerge and hybrid systems bridge legacy and digital systems. Expect growing adoption of asset-backed stablecoins for trade settlements, expansion of blockchain-based port community systems, and AI-enhanced smart contracts that automatically adjust to supply chain disruptions. This technological shift will ultimately create leaner, more resilient global shipping networks.
The integration of cryptocurrencies and blockchain in maritime transport and global trade is poised to expand significantly. Increasing regulatory clarity, technological advancements, and broader acceptance among international traders will likely drive this growth, making global maritime trade faster, cheaper, and more secure.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies represent a transformative force in maritime logistics and global trade. While there are challenges to overcome, the potential benefits make their adoption an attractive prospect for future-proofing international trade practices.
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies represent a paradigm shift for maritime trade, offering solutions to chronic inefficiencies while introducing new operational models. As the industry navigates initial adoption challenges, these technologies will increasingly underpin everything from cargo documentation to vessel fuel payments, fundamentally transforming how goods move across oceans in the digital age.



