Introduction to IoT in the Maritime Industry
The maritime industry is a critical component of the global economy, responsible for the transportation of approximately 90% of global trade. Technological advancements have been transforming the industry, and one of the most significant innovations is the Internet of Things (IoT). In this section, we will explore the definition of IoT, provide an overview of the maritime industry, and discuss the importance of IoT in the shipping industry.
1.1. Overview of the Maritime Industry
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices, sensors, and systems that collect, exchange, and analyze data to enable intelligent decision-making and automation. IoT devices can communicate with each other and with centralized control systems to provide real-time information, optimize processes, and facilitate remote monitoring and control.
The maritime industry encompasses a wide range of activities related to the transportation of goods, passengers, and resources via sea routes. It includes shipping companies, shipbuilders, ports, terminal operators, classification societies, maritime service providers, and regulatory bodies. The industry is characterized by complex supply chains, fluctuating market demands, stringent safety and environmental regulations, and significant operational challenges. As a result, the maritime industry is constantly seeking innovative solutions to enhance efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
1.2. Importance of IoT in the Shipping Industry
IoT plays a crucial role in the digital transformation of the shipping industry, offering numerous benefits and opportunities for optimization. Some of the key advantages of implementing IoT in the maritime industry include:
- Enhanced operational efficiency: IoT enables the collection and analysis of large volumes of real-time data, allowing shipping companies to monitor and optimize various aspects of vessel performance, such as fuel consumption, engine performance, and route planning. This results in reduced operating costs, increased productivity, and improved asset utilization.
- Improved safety and security: IoT devices can monitor various safety parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and vibration, enabling early detection of potential hazards and the implementation of preventive measures. Additionally, IoT can facilitate real-time tracking and monitoring of ships, containers, and cargo, improving the security of the entire supply chain.
- Better environmental compliance: The maritime industry faces increasing pressure to reduce its environmental impact, with stricter emissions regulations and sustainability standards. IoT solutions can help monitor and control emissions, waste disposal, and energy consumption, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and contributing to a greener shipping industry.
- Predictive maintenance: IoT-based condition monitoring systems can collect data on the health of various ship components and systems, enabling the early detection of potential failures and facilitating predictive maintenance. This results in reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and extended equipment life.
- Data-driven decision-making: The data collected and analyzed by IoT devices can provide valuable insights for shipping companies, enabling data-driven decision-making and enhancing overall business performance. This includes optimizing fleet management, cargo handling, and port operations, as well as improving the overall customer experience.
In summary, the introduction of IoT in the maritime industry has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of shipping operations. By leveraging the power of interconnected devices and data analytics, the industry can achieve significant improvements in efficiency, safety, sustainability, and overall business performance.

IoT Applications in the Maritime Industry
IoT technology has made a significant impact on the maritime industry, offering various applications that enhance efficiency, safety, and sustainability. In this section, we will discuss some of the key IoT applications in the maritime sector, including vessel performance monitoring, predictive maintenance, fleet management, navigation optimization, and safety and security.
2.1. Vessel Performance Monitoring and Optimization
IoT devices, such as sensors and data loggers, can be used to monitor and optimize vessel performance in real-time. By collecting and analyzing data from various ship systems, including propulsion, navigation, and auxiliary equipment, shipping companies can gain insights into fuel consumption, engine performance, and overall vessel efficiency. This information can be used to implement improvements, such as optimizing operational parameters, reducing energy consumption, and increasing the overall efficiency of the vessel.
2.2. Predictive Maintenance and Condition Monitoring
Predictive maintenance is an essential IoT application for the maritime industry, as it helps to minimize equipment downtime and reduce maintenance costs. IoT-based condition monitoring systems collect data on the health and performance of various ship components and systems, enabling early detection of potential failures. By analyzing this data, shipping companies can schedule maintenance activities more effectively, avoiding unexpected breakdowns and extending the lifespan of critical equipment.
2.3. Fleet Management and Asset Tracking
IoT technology can facilitate comprehensive fleet management and asset tracking by providing real-time information on the location, status, and performance of ships, containers, and cargo. IoT-enabled devices, such as GPS trackers, sensors, and communication systems, can be integrated into a centralized fleet management system, allowing shipping companies to monitor and control their assets remotely. This results in increased operational efficiency, improved cargo handling, and better utilization of resources.
2.4. Navigation and Route Optimization
IoT systems can optimize navigation and route planning by collecting and analyzing data on various factors, such as weather conditions, sea currents, fuel consumption, and vessel speed. By processing this data, shipping companies can identify the most efficient routes and adjust their course in real-time, minimizing fuel consumption and reducing transit times. Additionally, IoT technology can be used to enhance the accuracy and reliability of navigation systems, improving safety and reducing the risk of maritime accidents.
2.5. Safety and Security
Safety and security are paramount concerns in the maritime industry, and IoT applications play a vital role in enhancing both. IoT devices can monitor various safety parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and vibration, enabling early detection of potential hazards and the implementation of preventive measures. Additionally, IoT can facilitate real-time tracking and monitoring of ships, containers, and cargo, improving the security of the entire supply chain. IoT systems can also be used to detect and prevent unauthorized access to restricted areas, monitor crew activities, and ensure compliance with safety regulations. In summary, IoT applications have the potential to transform the maritime industry by providing valuable insights and enabling data-driven decision-making. By leveraging IoT technology, shipping companies can optimize vessel performance, implement predictive maintenance strategies, streamline fleet management, enhance navigation, and improve safety and security on board.
IoT Technologies and Devices in the Maritime Industry
In this section, we will discuss the various technologies and devices that enable IoT applications in the maritime industry, including sensors and data acquisition, wireless communication technologies, data analytics and machine learning, cloud computing and edge computing, and cybersecurity considerations.
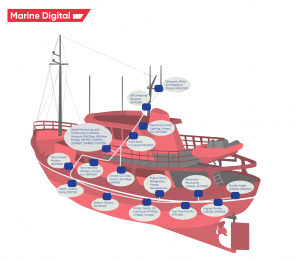
3.1. Sensors and Data Acquisition
Sensors are critical components of IoT systems in the maritime industry. They are responsible for collecting data from various ship systems and environmental factors. Examples of sensors used in maritime IoT applications include temperature, pressure, humidity, vibration, and GPS sensors. This data is then sent to data processing and analytics platforms for analysis and decision-making. Data acquisition systems are used to collect, store, and transmit sensor data, ensuring the integrity and reliability of the information.
3.2. Wireless Communication Technologies
Wireless communication technologies are essential for enabling seamless data transmission between IoT devices and systems in the maritime industry. Some common wireless communication technologies used in maritime IoT applications include Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Bluetooth, and cellular networks like 4G and 5G. Satellite communication systems, such as Inmarsat and Iridium, are also crucial for providing global coverage and ensuring reliable communication between ships and shore-based systems.
3.3. Data Analytics and Machine Learning
Data analytics and machine learning are vital components of IoT systems in the maritime industry. They enable the processing and analysis of vast amounts of data collected by IoT devices, providing valuable insights and facilitating data-driven decision-making. Machine learning algorithms can be used to identify patterns and trends in the data, enabling predictive maintenance, route optimization, and enhanced safety and security measures. Advanced analytics techniques, such as artificial intelligence (AI), can further improve the accuracy and efficiency of data analysis and decision-making processes.
3.4. Cloud Computing and Edge Computing
Cloud computing and edge computing are essential technologies for the implementation of IoT in the maritime industry. Cloud computing allows for the storage, processing, and analysis of data on remote servers, providing scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. This enables shipping companies to access and manage their IoT systems from any location, using any internet-enabled device. Edge computing, on the other hand, involves processing data closer to the source, such as on the ship itself. This can reduce latency and improve the efficiency of data processing, particularly when dealing with large volumes of data or when connectivity to the cloud is limited. Edge computing can also enhance data security by reducing the amount of sensitive information transmitted over networks.
3.5. Cybersecurity Considerations
As the maritime industry adopts IoT technologies and devices, cybersecurity becomes an increasingly important concern. Securing IoT systems and ensuring the privacy and integrity of data is crucial to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential cyber-attacks. Shipping companies need to implement robust cybersecurity measures, such as encryption, secure communication protocols, and regular security updates, to protect their IoT systems and the valuable data they generate. In conclusion, various technologies and devices enable IoT applications in the maritime industry, including sensors, wireless communication technologies, data analytics and machine learning, cloud computing and edge computing, and cybersecurity measures. These technologies work together to create connected, intelligent, and efficient systems that can revolutionize the shipping industry and drive innovation in the maritime sector.
Benefits and Challenges of Implementing IoT in the Maritime Industry
In this section, we will discuss the various benefits and challenges associated with implementing IoT in the maritime industry, focusing on operational efficiency and cost reduction, enhanced safety and security, improved environmental sustainability, data management and integration challenges, and regulatory and standardization issues.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction: IoT can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce costs in the maritime industry. By leveraging data from IoT devices, shipping companies can optimize vessel performance, reduce fuel consumption, and minimize equipment downtime. Predictive maintenance can help identify potential issues before they become critical, reducing the need for costly repairs and unscheduled maintenance. Furthermore, IoT can streamline fleet management and asset tracking, reducing operational overhead and improving overall fleet performance.
Enhanced Safety and Security: IoT technologies can also enhance safety and security in the maritime industry. Real-time monitoring of ships and their systems enables early detection of potential hazards or security breaches, allowing for timely and proactive responses. For instance, IoT sensors can monitor environmental conditions, detect gas leaks or fires, and automatically trigger alarms or safety systems. Moreover, advanced data analytics and machine learning can help predict and prevent accidents by analyzing historical data and identifying patterns or trends that may indicate an increased risk of incidents.
Improved Environmental Sustainability: IoT can play a crucial role in improving environmental sustainability in the maritime industry. By enabling more efficient vessel performance and route optimization, IoT can reduce fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. IoT technologies can also help shipping companies monitor and manage their environmental impact, such as monitoring emissions, waste disposal, and ballast water management. This can help companies comply with environmental regulations, reduce their environmental footprint, and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
Data Management and Integration Challenges: Despite the numerous benefits of IoT in the maritime industry, there are challenges associated with data management and integration. IoT systems generate vast amounts of data that need to be collected, stored, processed, and analyzed. Integrating this data across different systems and devices, as well as with existing IT infrastructure, can be complex and time-consuming. Ensuring data privacy and security is also critical, as data breaches and unauthorized access can have severe consequences for shipping companies. Overcoming these challenges requires effective data management strategies, robust cybersecurity measures, and the implementation of industry standards and best practices.
Regulatory and Standardization Issues: Implementing IoT in the maritime industry also involves navigating regulatory and standardization issues. As the adoption of IoT technologies accelerates, there is a growing need for consistent standards and regulations to ensure interoperability, security, and reliability. Shipping companies must comply with international and regional regulations, such as those set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and other governing bodies. This can be challenging, as regulations may vary between regions, and keeping up with the rapidly evolving technology landscape can be difficult. In addition, the lack of standardization can hinder collaboration and data sharing between different stakeholders in the maritime industry.
In conclusion, IoT has the potential to revolutionize the maritime industry by offering numerous benefits, including operational efficiency, cost reduction, enhanced safety and security, and improved environmental sustainability. However, shipping companies must also address challenges related to data management, integration, and regulatory and standardization issues to ensure the successful implementation of IoT technologies in their operations.
Case Studies: Successful IoT Implementations in the Maritime Industry
In this section, we will discuss successful IoT implementations in the maritime industry, focusing on three case studies: smart container tracking and monitoring, autonomous vessels and remote operations, and IoT-based port management solutions.
Smart Container Tracking and Monitoring
IoT has revolutionized container tracking and monitoring, providing real-time information on the location, temperature, humidity, and other conditions of cargo containers. One notable example is the collaboration between Maersk Line, the world’s largest container shipping company, and Ericsson. They developed a remote container management system using IoT technology to track and monitor over 270,000 refrigerated containers. The system uses GPS, GSM, and satellite communications to provide real-time data, enabling more efficient logistics management, reducing spoilage of perishable goods, and improving overall supply chain visibility.
Autonomous Vessels and Remote Operations
IoT is paving the way for autonomous vessels and remote operations in the maritime industry. One example is the Yara Birkeland, the world’s first fully electric and autonomous container ship. Developed by Norwegian company Yara International and technology firm Kongsberg, the Yara Birkeland uses IoT sensors, cameras, and advanced algorithms to navigate and operate autonomously. The vessel can reduce emissions by replacing 40,000 truck journeys annually and has the potential to transform the shipping industry by reducing costs, improving safety, and minimizing environmental impact. Another example is Rolls-Royce’s Intelligent Awareness System, which uses IoT sensors, cameras, and machine learning to enhance situational awareness and enable remote ship operations. This system has been successfully tested on several vessels, including the Finferries’ double-ended car ferry Falco, demonstrating the potential of IoT technologies in enabling autonomous and remote-controlled maritime operations.
IoT-based Port Management Solutions
IoT technologies have also been applied to improve port management and operations. One example is the Port of Rotterdam, Europe’s largest port, which has implemented an IoT-based platform to optimize logistics and traffic management. The platform collects data from IoT sensors, cameras, and other devices, enabling real-time monitoring of vessel locations, port infrastructure, and environmental conditions. This information is used to optimize scheduling and resource allocation, reducing waiting times and increasing overall port efficiency. Another example is the Port of Singapore, one of the busiest ports globally, which has developed an IoT-based Maritime Single Window system. This system streamlines and automates the submission of regulatory documents and facilitates data exchange between various stakeholders, such as shipping companies, port operators, and regulatory authorities. By leveraging IoT technologies, the Port of Singapore can improve operational efficiency, enhance safety and security, and promote greater collaboration between maritime industry stakeholders.
These case studies demonstrate the transformative potential of IoT in the maritime industry, highlighting the numerous benefits and applications across various aspects of shipping, port management, and logistics. As IoT technologies continue to advance, it is likely that we will see even more innovative solutions and applications in the maritime sector, driving further improvements in efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
The Future of IoT in the Maritime Industry
In this section, we will explore the future of IoT in the maritime industry, focusing on emerging IoT technologies and trends, the role of 5G in maritime IoT applications, and the impact of digital twin technology on ship design and operations.
6.1. Emerging IoT Technologies and Trends
As IoT technologies continue to advance, we can expect to see new applications and innovations in the maritime sector. Some of the emerging trends include:
- Advanced sensor technology: Developments in sensor technology, such as miniaturization, increased accuracy, and lower power consumption, will enable more comprehensive data collection and monitoring in the maritime environment.
- Integration of IoT with other technologies: The convergence of IoT with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and augmented reality, will lead to more sophisticated solutions for logistics, fleet management, and asset tracking.
- Improved connectivity: Satellite and other communication technologies will provide better coverage and connectivity, even in remote maritime areas, enabling more reliable data transmission and real-time monitoring.
- Increased focus on data security: As the amount of data collected and exchanged in maritime IoT applications grows, there will be a greater emphasis on ensuring data security and privacy to protect against cyber threats.
6.2. The Role of 5G in Maritime IoT Applications
5G, the fifth generation of mobile networks, is poised to play a significant role in maritime IoT applications due to its high data rates, low latency, and increased capacity. The benefits of 5G for the maritime industry include:
- Enhanced real-time data transmission: 5G’s increased data rates and lower latency will enable faster and more reliable data transmission, allowing real-time remote monitoring and control of maritime operations.
- Improved connectivity for autonomous vessels: 5G networks will provide the necessary communication infrastructure for autonomous vessels, facilitating the exchange of data between ships and shore-based control centers.
- Support for a greater number of connected devices: With its increased capacity, 5G can support a larger number of connected devices, making it ideal for large-scale IoT deployments in the maritime sector.
6.3. Digital Twin Technology for Ship Design and Operations
Digital twin technology, which involves creating a virtual replica of a physical asset, is gaining traction in the maritime industry for ship design and operations. By integrating IoT sensors and data analytics, digital twins can provide real-time information on a ship’s performance, maintenance needs, and other aspects of its operation. Key benefits of digital twin technology in the maritime industry include:
- Improved ship design: Digital twins can be used during the design phase to simulate and optimize ship performance under various conditions, leading to more efficient and sustainable vessel designs.
- Enhanced predictive maintenance: By monitoring the real-time performance of a ship’s components, digital twins can identify potential issues before they become critical, allowing for proactive maintenance and reduced downtime.
- Optimized operations: Digital twins can help optimize a ship’s route, speed, and other operational parameters, leading to improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and lower operating costs.
In conclusion, the future of IoT in the maritime industry looks promising, with new technologies and trends poised to drive further innovation and improvements in efficiency, safety, and sustainability. As the sector continues to embrace IoT, we can expect to see significant transformations in the way ships are designed, built, and operated.

Conclusion: The Impact of IoT on the Maritime Industry and Future Outlook
The Internet of Things (IoT) has the potential to revolutionize the maritime industry by offering new opportunities for improving efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability. As we have seen throughout this discussion, IoT applications and technologies have already made significant strides in various areas of the maritime sector, from vessel performance monitoring and optimization to autonomous vessels and port management.
The impact of IoT on the maritime industry can be summarized through the following key points:
- Operational efficiency and cost reduction: IoT enables the real-time monitoring and analysis of vessel performance, helping to optimize fuel consumption, reduce downtime, and minimize maintenance costs. Additionally, IoT-based fleet management and asset tracking solutions can streamline logistics and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
- Enhanced safety and security: IoT technologies can help improve the safety and security of maritime operations through real-time monitoring of vessel conditions, crew health, and cargo security. Advanced sensor systems and data analytics can also help detect potential threats and vulnerabilities, allowing for timely responses and mitigations.
- Improved environmental sustainability: IoT applications, such as route optimization and energy-efficient vessel operations, can contribute to reducing the environmental impact of the maritime industry. IoT can also help monitor and enforce compliance with environmental regulations, such as emissions standards and ballast water management.
- Accelerated innovation and digital transformation: The integration of IoT with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and 5G, will drive further innovation and enable the development of new solutions and business models in the maritime sector. This digital transformation will reshape the industry, making it more competitive, responsive, and resilient.
However, the successful implementation and widespread adoption of IoT in the maritime industry will depend on overcoming various challenges, including data management and integration, cybersecurity concerns, and regulatory and standardization issues. Collaboration between industry stakeholders, technology providers, and regulatory bodies will be critical in addressing these challenges and ensuring that IoT technologies are harnessed effectively and responsibly.
In the future, we can expect the continued growth and evolution of IoT applications in the maritime sector, with new technologies and trends further enhancing the industry’s capabilities. The convergence of IoT with other emerging technologies, such as digital twins and 5G, will likely play a significant role in shaping the future of the maritime industry, unlocking new possibilities for innovation and sustainable growth.
Ultimately, the impact of IoT on the maritime industry will be transformative, driving significant improvements in efficiency, safety, and environmental performance. As the industry embraces IoT and navigates the challenges associated with its adoption, the potential for a more connected, intelligent, and sustainable maritime future becomes increasingly apparent.
Prepared by MaritimEducation team.

